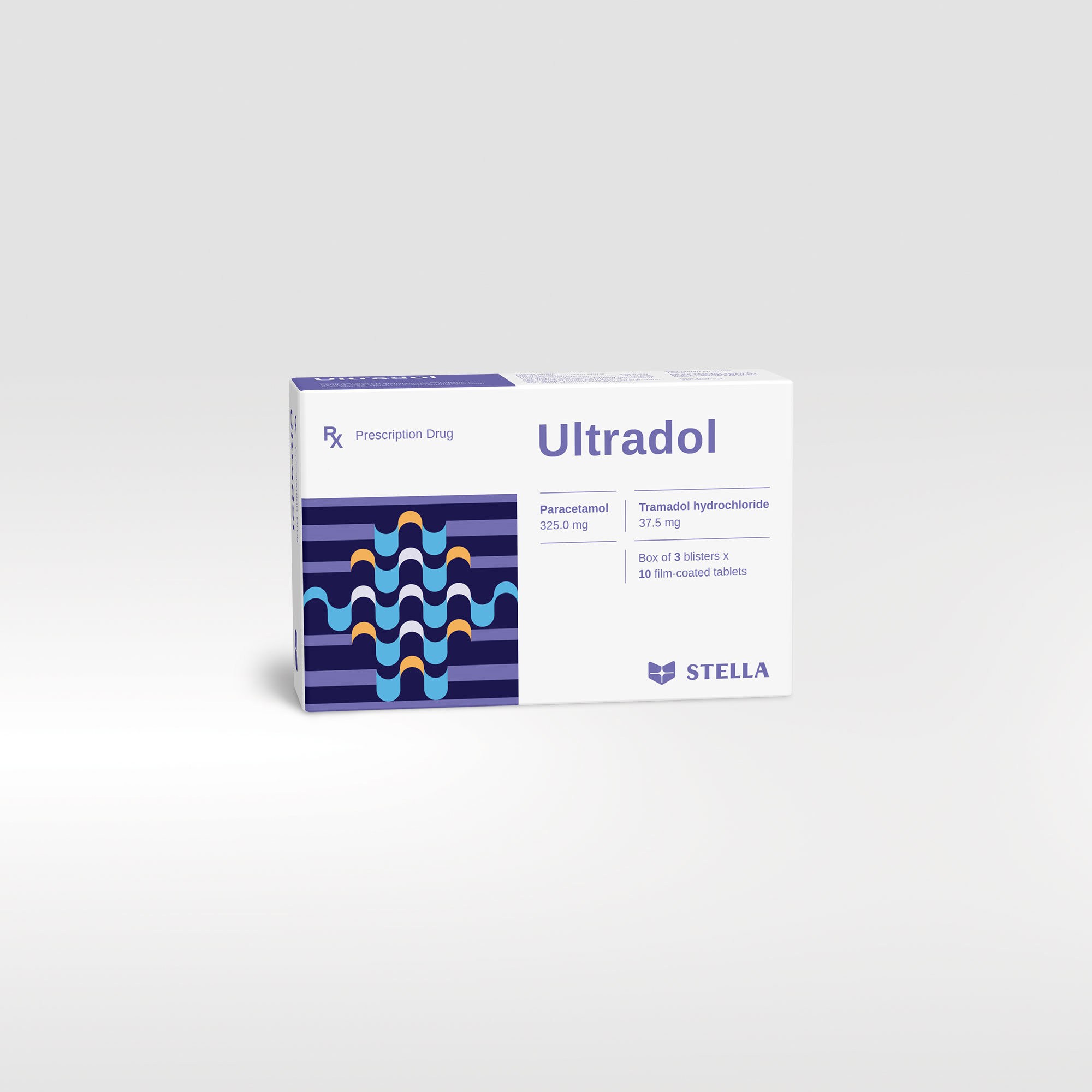
Ultradol Rx
Tramadol is an analgesic that acts on the central nervous system, which affects the brain and changes the body’s sensations and response to pain. Meanwhile, paracetamol is a common active ingredient used to relieve pain and reduce fever. When tramadol and paracetamol are combined, Ultradol is effective in reducing moderate to severe pain.
| Pack size | Box of 20 tablets, 30 tablets |
| Shelf-life | 24 months |
| Composition | Paracetamol, Tramadol hydrochloride |
| Dosage forms and strengths | Film-coated tablet: Paracetamol 325 mg, Tramadol hydrochloride 37.5 mg |
Product code :